BACK PAIN TREATMENT IN MUMBAI
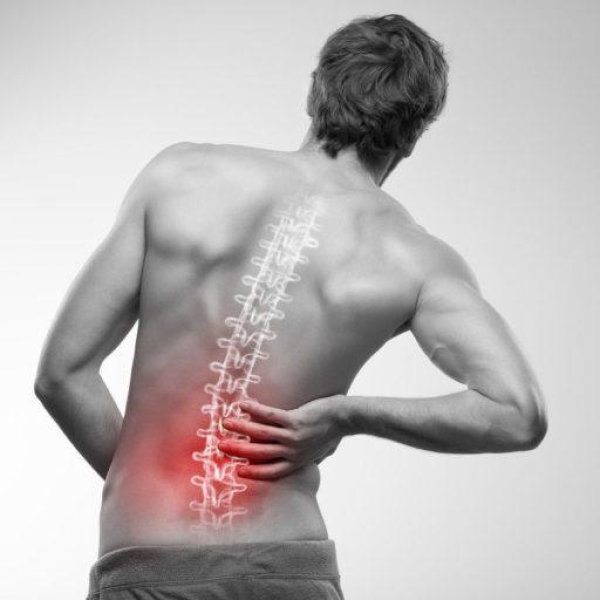
Table of Contents
- What causes back pain?
- Diagnosis for back pain
- Risk factors associated with back pain
- When to see your doctor?
- Back Pain Treatment in Mumbai
- Why Choose Dr. Saijyot Raut for Back Pain Treatment in Mumbai?
Back pain is one of the most common complaints due to which people get absent from work or seek medical help. Unfortunately, sometimes this pain is severe and worsens with time in most cases. Back pain can range from a muscle aching to shooting or burning sensations in the lower body.
What causes back pain?
Back pain results from injury, activity, and some medical conditions. Given below are the causes of back pain as recognized by the experts:
Strain
Strain is the most obvious factor that gives rise to back pain. Strain can be a result of repeated heavy lifting or an abrupt awkward movement. Over-activity can also strain back muscles and spinal ligaments.
Poor posture
Many times back pain is caused due to everyday activities and poor posture. Such activities include working out too much, prolonged sitting or lying down, sleeping in an uncomfortable position, or wearing a poorly fitting backpack.
The spine is made of interlocked vertebrae with interbody discs. Herniated or ruptured discs often result in severe back pain. Though herniated discs can happen in any part of the spine, they are most common in the lower part of the backbone.
Degenerative Changes
Degenerative changes in the spine refer to the osteoarthritis of the spine. It occurs when the cushioning of the spine begins to wear away due to overuse. It is most common in older adults.
Medical problems
Several medical conditions such as kidney and spine infections and sleep disorders also contribute to back pain.
Diagnosis for back pain
Physical examination: After studying the symptoms and medical history, a physical examination of the patient is performed. During the physical test, the doctor examines your back and assesses your ability to sit, stand, walk, and left your legs. It is done to understand better the muscle strength, reflexes, and neurological condition of the patient.
Imaging studies: When a specific condition is suspected of giving rise to back pain, imaging studies narrow down the cause. Given below are some of the imaging technologies:
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)– MRI scans use magnetic fields to generate detailed images of bones and soft tissues like muscles, ligaments, or intervertebral discs.
X-ray: X-rays use electromagnetic radiation to show a good picture of the back’s bone. Plain x-rays can’t detect herniated discs, but they can reveal areas in your back where bone spurs or other degenerative changes might pinch your nerves or spinal cord.
CT (Computerized tomography) Scan: These are used to generate more detailed pictures of the spinal column by taking a series of x-rays from different directions and combining them to create cross-sectional images.
BMD Dexa scan: A DEXA scan is used to measure bone density. It can provide helpful details about your risk for osteoporosis (bone loss) and fractures.
Blood tests: Blood and urine tests can help determine the underlying conditions, such as inflammation and infection, causing back pain.
Bone scan: A bone scan is performed in rare cases to look for abnormalities, such as tumors in bone tissue.
Risk factors associated with back pain
Given below are the factors that might put you at greater risk of developing back pain:
- Age: The risk of having back pain increases with age. According to studies, it is more common in people who are more than 30 years old.
- Improper lifting techniques: Back pain can occur if you use your back instead of your legs to lift weights.
- Excess weight: Excess body weight, which puts extra pressure on the back, can also cause back pain.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant women often tend to suffer from pain in the back.
- Poor physical fitness: One of the leading risk factors that could potentially expose you to back pain is the lack of physical activity. Lack of exercise weakens the abdomen and back muscles.
- Diseases: Medical issues such as osteoporosis and arthritis often cause back pain.
- Smoking: It is found that the risk of developing back pain increases with the number of cigarettes smoked per day.
When to see your doctor?
According to studies, 90 percent of back pain gets better within six months, and they can be cured with some exercise and painkillers. But if it doesn’t, there may be a more serious underlying cause behind it. Given below are the symptoms associated with back pain that should prompt you to immediate medical attention;
- Very severe pain that doesn’t go away with rest
- Swelling on the back
- Loss of sensation in the legs
- Pain when urinating
- Radicular leg pain
- Weakness, numbness, or tingling in legs
- Loss of control over bowel movements
- Fever and weight loss
Back Pain Treatment
The following treatment methods are provided and advised to the patients with back pain:
Medications
Back pain can be cured by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen. Other prescribed medications include topical rubs, ointments, opioids, muscle relaxants, and epidural steroid injections.
Physical Therapy
Given below are the therapies that often work for a patient with back pain:
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture is considered a successful therapy for chronic back pain. It applies to either lower or upper back pain. This therapy works by maintaining the healthy flow of your body’s energy force to relieve the pain.
- Massage: Massages may be useful when it comes to ease short-term lower back pain. They help in muscle relaxation and reduce pain and inflammation. Shiatsu massage is considered to be very effective for lower back pain.
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) involves placing electrodes on your skin near the painful areas to deliver small amounts of electrical stimulation that may eliminate pain.
Rehab
The term ‘Rehab’ is most commonly used to refer to residential drug rehabilitation. Rehab is a process designed to help a person recover from illness of back pain. It may include physical therapy, group counseling, or drug treatment. If you get rehab when your back problems first show up, you might be able to avoid surgery.
Surgery
Surgeries for back pain are usually recommended in case of those structural abnormalities which don’t respond to the medications and therapies. The surgeries aim to cure symptoms such as numbness and persistent pain in the legs caused by stressed nerves in the spine. These decompression surgeries work by removing a bone spur or a herniated portion of the disc that presses on the nerve root from the spinal column. Given below are some decompression surgeries that are performed for back pain treatment in Mumbai:
A laminectomy is most commonly performed to treat lumbar spinal stenosis symptoms. However, it is also done when nerve damage symptoms accompany the pain. Laminectomy involves a small incision to create an opening in the lamina (vertebral arch) to relieve pressure on your nerve roots.
Microdiscectomy or Discectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed on patients with a herniated disc. This surgery involves first making a small incision at the level of the disk herniation. Then the surgeon removes the portions of the herniated disc to relieve pressure on the spinal nerve column.
Dr. Saijyot Raut is one of the most renowned surgeons for back pain treatment in Mumbai. He provides consultations for all spine conditions and advises patients in the best and most ethical form. He is a life member of the AO spine, Association of spine surgery India, and the International Society of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology. In addition, he is highly revered for offering cost-effective solutions for all back pain problems.
Back Pain FAQ
A spine doctor usually performs the following tests:
- Range of motion test to check back mobility
- Nerve tests to check neurological functioning
- Palpation tests to spot the source of pain
- Blood and urine tests to rule out other problems, like an infection or a kidney stone
- Imaging tests like X-rays and MRIs for diagnosing ongoing pain due to a back injury, nerve problems, or persistent fever
Follow these habits to prevent back pain
- Always stretch before and after workouts or any other physical activity
- When sitting: keep your posture straight, use lower back support, and balance your weight on both legs at all times
- Buy a firm mattress if you don’t already have one with an adequately firm pillow
- Keep your weight close to your BMI
- Avoid heavy weight lifting, and always use your leg strength to lift instead of moving your back
- Avoid smoking as spine degeneration is one of its negative effects
Ask these questions when consulting your spine doctor online or in-office:
- What is causing or worsening my back pain?
- Would surgery be necessary? Are there alternative treatments?
- What other symptoms or health problems can my back pain lead to?
- How long will it take to treat my back pain condition?
- Where can I learn more about managing my back pain in routine life?
A survey conducted by AAPM&R suggests that about one in two people believe that back pain requires surgical treatment. But according to spinal experts, just 5% of back pain cases will be effectively helped by surgery. Hence, experts always exhaust all non-surgical options for back pain treatment before recommending surgery.
You should reach out to a spine specialist when:
- Your back pain persists for three months or more
- Your back pain radiates to other parts of your body
- You have a limited range of back motion with motor weakness, numbness, or tingling
- You have a back injury or accident
- You experience loss of bladder or bowel control with back pain
- You have back pain that worsens at night
Chronic Low Back Pain is when you have persistent or fluctuating pain in your lower back for longer than three months.
Connection Between Your Spine & CLBP
- Your lower back has vertebrae of the lumbar spine that allows forward and backward, as well as twisting movements
- The two lowest segments in the lumbar spine, L5-S1 and L4-L5, carry the most weight and have the most movement, making the area prone to injury.

- Non-specific: No obvious cause
- Traumatic Injuries: Sports, car accidents, or a fall injuring tendons, ligaments, or muscle
Vertebral Disk Problems: Herniated or ruptured discs, disc degeneration
Abnormal Curvature of the spine: Scoliosis or kyphosis.
Medical problems: Fibromyalgia (musculoskeletal
pain) or rheumatoid arthritis (joint pain)
- Age: More common with advancing age and between ages of 30 and 50.
Fitness level: Inactive people with weak back and abdominal muscles may not properly support the
Job-related factors: Jobs requiring heavy lifting, pushing, or pulling, working at a desk
Weight Gain: being overweight or obese puts stress on the back
- Psychological factors: Anxiety, depression, mood, stress can influence the likelihood of experiencing back pain
- Smoking: It can restrict blood flow and oxygen to the discs, causing them to degenerate faster.
- Pain in the lower area of the back
Mobility impairment
- Radiating pain in the lower
- Difficulty in carrying out daily activities
- Difficulty to maintain a standing, sitting or a lying position, especially in case of radiating pain to the lower extremities bending
Diagnosis of CLBP is based on history, symptoms, physical examination and results of diagnostic studies.
When simple treatments are ineffective, your doctor may order imaging studies of the lower back, which may include
- Computed Tomography Scan (CT/CAT scan),
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Selective Nerve Root Block
- Discography
- X-rays
- Myelography
CLBP is treated by identifying the cause with a stepped care approach, moving from simple low-cost treatments to more aggressive approaches.
- Medications prescribed by doctor
Hot or cold packs application
Resuming normal activities to ease pain (bed rest not recommended)
Exercises to strengthen core and back muscles
Psychological support
Manual therapy by Chiropractors, Osteopaths or Physiotherapists
Surgery for back pain (recommended if there’s a specific medical reason and when other treatments have not helped
- Simple back exercises and stretches can help reduce back pain. Here are some exercises that will help you relieve CLBP.

The Kneeling Stretch
Kneel on the floor, legs spread
- hip-width apart.
- Sit back on your heels and drop your head down.
- Feel the stretch
- Lift your head up and return to the starting position through your
- Repeat 5 times.

The Knee-to-chest Stretch
- Lie on your back with your knees bent and your feet flat on the floor.
- Using both hands, pull and hold both knees to your chest until you feel a slight stretch in your lower back.
- Release your knees and return to the starting position.
- Repeat 5 times.
The Back Extension

- Lie on your chest with your hips flat.
- Using both hands, push your hands off lifting your head and shoulders.
- Arch your back, straighten your elbows to feel the stretch in the lower back area.
- Return to the starting position.
- Repeat 5 times.
The Plank

- Get into your forearms on the ground.
- Keeping your elbows in line with your shoulders, push up onto your forearms and toes, keeping your back straight and your elbows on the ground.
- Hold for a few seconds, and then lower yourself to the floor.
The Cat-Cow

- Get on your hands and knees, keeping your back straight.
- Round your lower back as much as you can toward the ceiling.
- Then arch your back so that your stomach comes toward the floor.
- Repeat 10 times.
Always check first with your doctor before starting an exercise program and get a list of helpful exercises.
One Spine Clinic - Best Spine Surgeon in Khar


